While you may enjoy more of a financial buffer compared to others, inflation can still throw a wrench into your short-term plans. We ask the question “how does inflation affect investments?” and take look at what inflation means to business growth, how you can avoid the impact of inflation on your investments and assess some smart strategies to stay ahead of the curve.
What is Inflation?
As a simple definition of inflation, you could say it is a measurement of a rise in the general price of goods and services. As prices rise, this erodes the purchasing power of cash and certain investments.
For people with a high net worth, it has an immediate impact.
Influence of Inflation
Reduced Buying Power – Increased Cost of Living
Say you’ve got a $100,000 investment earning 2% interest annually, as inflation hits 5% inflation, your real return goes negative (-3%). Not only does your earning power go down, but everything – including travel and luxury goods – sees a price hike. So, your money also buys less, impacting any day-to-day expenses and planned purchases. This could put a strain on your discretionary spending and may even force adjustments to your lifestyle.
Investment Strategies to Mitigate Inflation
You probably have a wider array of investment options to hedge against inflation than most. Here are some key strategies that you could:
Real Assets: If you invest in assets whose value tends to rise with inflation – like real estate (land, rental properties), commodities (precious metals, oil), and infrastructure (toll roads, utilities) you may be able to outpace inflation as their prices rise faster. Commodities like gold are ‘inflation hedges’ – their demand tends to increase during periods of economic uncertainty.
Stocks with Inflation-Beating Potential: Not all stocks are created equal. You’ll need to look for companies with strong pricing power – meaning they can raise prices to maintain their profit margins despite inflation. These are often established companies in essential sectors like consumer staples (food, beverages), healthcare, and utilities.
Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS): These government bonds see their principal value adjust based on inflation, ensuring investors receive their purchasing power back at maturity. While the interest rates may be lower than traditional bonds, they provide a guaranteed inflation hedge.
Diversification is Key
Don’t put all your eggs in one basket! Investing in well-managed, diversified portfolios helps mitigate risk and capture potential gains from different sectors. Our range of investment types span across property, alternatives & more.
How does Inflation Affect Investments?
We explore both the short and long term effects:
Short-Term Adjustments
Smart investment strategies are crucial, but you might also want to adapt some spending habits to navigate the effects of inflation:
Review Expenses: Look at your recurring costs and identify areas for potential cuts. Consider renegotiating or fixing financial arrangements, look for savings, and reduce any non-essential spending.
Prepay for Future Needs: If you know a large expense is coming up – new car purchase, substantial home renovation – you should act now. Prepaying with currently available funds will avoid the inflated cost later.
Focus on Cash Flow: Short-term investments with high liquidity can be helpful to cover immediate expenses or take advantage of sudden investment opportunities.
Seek Professional Advice: Trusted financial advisors give you far more personalised strategies based on your individual circumstances and risk tolerance.
Long-Term Considerations
Inflationary periods tend to be cyclical. While the short-term impact needs attention, you are going to need to look at long-term wealth preservation too:
Focus on Growth Assets: Investments in high-potential growth businesses – particularly those with a history of substantial dividend growth, can provide a hedge against inflation while offering the potential for significant returns over an extended period.
Maintain a Diversified Portfolio: Now is a good time to rebalance your portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation and ensure long-term growth prospects. Remember, inflation is a marathon, not a sprint. By having a well-defined strategy, you can navigate the short-term challenges and ensure their wealth continues to grow over the long term. Learn more about what diversification in investing is here.
Inflation can lead to various economic scenarios, including stagflation, where high inflation coincides with stagnant economic growth and high unemployment. This combination poses unique challenges for investors, as traditional investment strategies may not perform as expected under such conditions.
Additional Considerations
Watch out for taxes: Inflation can push individuals into higher tax brackets, and you may need expert financial advice to minimise your tax burden.
Global Diversification: Investing in companies and assets in different countries can offer diversification benefits and mitigate the impact of inflation specific to one region.
Alternative Investments: Explore alternative asset classes like private equity, venture capital, or hedge funds. With the right professional guidance, these can offer higher potential returns.
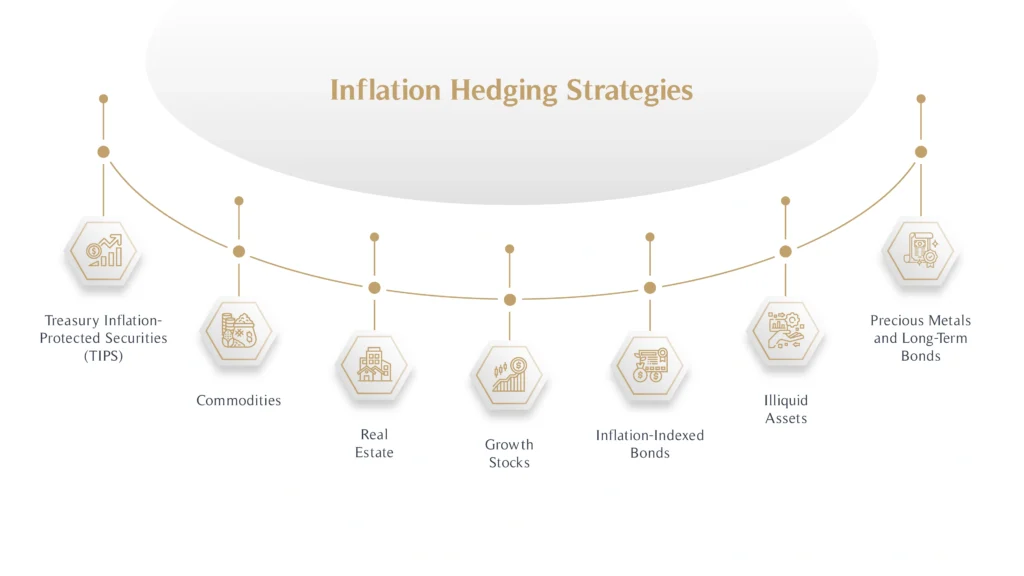
Inflation Hedging Strategies
Inflation can erode the value of your investments, but with the right strategies, you can protect your wealth and even capitalise on inflationary pressures.
Below are some effective approaches for hedging against inflation and safeguarding your financial future:
1. Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS)
TIPS are government-issued bonds designed specifically to shield investors from inflation. Unlike traditional bonds, the principal value of TIPS adjusts with inflation, ensuring your purchasing power remains intact. To understand how these securities fit within broader asset classes, check out our guide on What is an Asset Class?
2. Commodities
Investing in commodities like gold, silver, and oil can offer excellent protection against inflation. These assets tend to increase in value as inflation rises, making them ideal inflation hedges. Precious metals, in particular, are often seen as safe havens during times of economic uncertainty.
3. Real Estate
Real estate is another strong hedge against inflation. Properties, whether residential or commercial, often appreciate in value over time and generate income that keeps pace with inflation. Additionally, income-generating real estate, such as rental properties, provides cash flow that adjusts with rising costs, protecting your purchasing power.
4. Growth Stocks
Investing in growth-oriented companies with pricing power can help offset inflation’s impact. These businesses, often in sectors like technology, healthcare, and consumer goods, can pass on higher costs to customers, maintaining or growing their profit margins.
5. Inflation-Indexed Bonds
Inflation-indexed bonds, such as TIPS, offer another layer of protection for your portfolio. These bonds are structured to ensure their value keeps pace with inflation, providing stability during volatile economic periods.
6. Illiquid Assets
Illiquid assets like private equity or infrastructure investments can serve as long-term inflation hedges. These assets are less affected by short-term market fluctuations and often provide higher returns that outpace inflation over time.
7. Precious Metals and Long-Term Bonds
Beyond commodities, long-term bonds with inflation-adjusted yields can also protect your portfolio. Investing in a mix of precious metals and bonds ensures diversification and reduces risk.
By incorporating these inflation-hedging strategies into your portfolio, you can preserve your wealth and stay ahead of rising prices.
Inflation and Savings
Inflation doesn’t just impact investments—it can also erode the value of your savings, making it crucial to adapt your financial strategy to maintain purchasing power.
Here’s how inflation affects savings and steps you can take to protect them:
1. The Impact of Inflation on Savings
Inflation reduces the purchasing power of your money. For example, if inflation rises by 5%, the value of every pound or dollar saved in a low-interest account effectively decreases. Over time, this erosion can significantly impact your net worth and financial security.
2. Low-Interest Savings Accounts
Traditional savings accounts often offer interest rates that fail to keep up with inflation. As a result, money kept in these accounts may lose value over time. Instead, consider shifting funds into accounts with higher returns.
3. Certificates of Deposit (CDs) and Money Market Funds
While fixed investments like CDs provide stability, their returns are typically low, leaving them vulnerable to inflation. Money market funds, which offer higher liquidity, may be a better option during inflationary periods, as they often provide competitive returns without locking your money away.
4. Liquid Assets
Maintaining liquid assets is essential to meet immediate expenses, but it’s important to ensure these assets are earning enough to counteract inflation. Investing in higher-yielding accounts or short-term instruments can help mitigate losses.
5. Wage and Price Controls
Inflation not only affects savings but also wages. If your income doesn’t rise with inflation, the gap between your earnings and expenses widens. Exploring alternative income sources or renegotiating salary terms can help bridge this gap.
Learn more about how inflation, interest rates, and investment returns are interconnected by exploring our article on How Does Interest Rate Affect Investment?.
Inflation’s Effect on Borrowers and Lenders
Inflation can have contrasting effects on borrowers and lenders, creating unique opportunities and challenges depending on which side of the equation you fall.
1. Borrowers Benefit from Inflation
Borrowers often gain during inflationary periods because the value of the money they repay decreases over time. For instance, if you take out a loan at a fixed interest rate, inflation reduces the real cost of your repayments. This makes borrowing for investments, like real estate or business expansion, more appealing during inflation.
2. Lenders Face Challenges
Conversely, lenders lose purchasing power as the money they are repaid holds less value. To counteract this, lenders may charge higher interest rates to offset the impact of inflation, increasing borrowing costs for future loans.
3. Dynamics Between Inflation Rates and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates are closely linked. Rising inflation typically leads to higher interest rates, which can affect the cost of borrowing and the return on lending. For example, inflation-linked bonds (ILBs) adjust their payouts to align with inflation, offering protection to lenders.
4. Cash Flow and Rent Increases
For borrowers using loans to invest in income-generating assets, inflation can be advantageous. For instance, landlords may increase rents in response to inflation, boosting cash flow and offsetting higher borrowing costs.
Understanding the dynamics between inflation, borrowers, and lenders allows you to make informed decisions about loans, investments, and interest-sensitive assets.
Inflation’s Impact on Asset Classes
Inflation affects asset classes differently, creating risks for some and opportunities for others. Here’s how various asset types respond to inflationary pressures:
1. Stocks
Stock prices may fluctuate during inflation, but companies with pricing power and essential products often fare well. High-growth sectors and dividend-paying stocks can also provide a buffer against inflation.
2. Bonds
Long-term bonds are particularly vulnerable to inflation, as their fixed payouts lose value over time. Conversely, inflation-linked bonds like TIPS adjust their principal and payouts, making them a safer choice during inflationary periods.
3. Real Estate
Both residential and industrial real estate typically perform well during inflation. Rising property values and rental income provide a natural hedge against rising costs.
4. Commodities
Commodities like oil, gold, and agricultural products often see price increases during inflation, making them a reliable asset class for diversification.
5. Fixed-Income Securities
Fixed-income securities, such as annuities, face challenges as inflation reduces the real value of their payouts. Diversifying with inflation-adjusted options can help mitigate this risk.
To see how inflation plays a role across different types of investments, review our comprehensive guide on What is an Asset Class?.
Planning for Inflation
A proactive approach to financial planning can help you navigate inflation and its long-term effects. Here’s how to stay ahead:
1. Diversify Your Portfolio
Asset allocation across different sectors, regions, and asset types helps reduce risk and captures growth opportunities during inflation.
2. Explore Alternative Investments
Consider inflation-resistant options like private equity, hedge funds, or high-growth investments. These assets offer higher return potential but require professional guidance.
3. Adjust Long-Term Financial Plans
Revisit your financial strategy to account for inflation’s impact. This may involve increasing your investment in inflation-protected securities or reallocating funds to growth-oriented assets.
Inflation doesn’t have to derail your financial goals. With the right planning and strategies, you can turn inflation into an opportunity to strengthen your wealth.
Expert Insights
As financial advisors at MHG Wealth, we often hear the same question from clients: “How do I protect my investments when interest rates are unpredictable?” The answer isn’t about reacting to every rate hike or cut – it’s about having a well-structured plan that evolves with the market. Here’s our take, rooted in years of experience and real-world examples.
Understanding Interest Rate Trends
Interest rates aren’t just numbers – they reflect economic trends, central bank policies, and market sentiment.
Here’s how we guide clients:
- Stay Calm, Stay Focused:
When interest rates began rising sharply post-pandemic, many investors panicked, pulling money out of the markets. One of our clients, a successful entrepreneur, was tempted to sell his bond portfolio at a loss. We encouraged patience and reallocated his funds into shorter-duration bonds and dividend-paying stocks, which weathered the storm. The result? He not only preserved his wealth but grew it when markets stabilised. - Look for Hidden Opportunities:
Rising interest rates often impact certain sectors more than others. For instance, during the last rate hike cycle, our team identified a surge in demand for consumer staples—companies offering essential goods that people buy regardless of economic conditions. By shifting a portion of our clients’ equity portfolios into this sector, we delivered steady growth even as other parts of the market cooled.
Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1: Two Bond Investors
Two clients approached us in 2022, both holding significant investments in government bonds as interest rates were climbing.
- Investor A was concerned about the falling value of his long-term bonds. We recommended a shift into floating-rate bonds, which offer yields that adjust with rising rates. This strategy allowed his portfolio to keep pace with rate changes without locking in losses.
- Investor B, held a mix of long and short-term gilts. Rather than recommending a complete overhaul, we suggested trimming their long-term gilt holdings and diversifying into inflation-linked gilts. This balanced strategy helped cushion the impact of rising inflation while ensuring steady and reliable returns.
Both clients benefited from tailored strategies that matched their risk tolerance and goals, proving that interest rate changes are manageable with the right guidance.
Scenario 2: Real Estate Opportunities in a High-Rate Environment
Interest rates directly affect mortgage costs, which in turn impact real estate investments. One of our clients, a retired professional with a property portfolio, was concerned about declining rental demand during a high-rate period.
We worked with him to:
- Reevaluate Rental Pricing: By adjusting rental prices slightly to align with market trends, he maintained occupancy rates.
- Invest in Real Assets: He diversified into real estate investment trusts (REITs) focused on sectors like healthcare and industrial properties, which tend to perform well regardless of rate changes.
This proactive approach ensured steady cash flow while positioning him for future growth when rates stabilised.
Inflationary periods demand action. With the right advice, and by understanding how inflation affects your finances, you will be able to implement a combination of investment strategies and spending adaptations, that not only maintain your lifestyle and purchasing power but also position your wealth for very sustainable growth as the inflationary cycle becomes more typical. If you would like to speak with an experienced financial advisor, please contact us at MHG Wealth today.