Investing is a strategic way to grow wealth, preserve capital, and plan for financial security. Traditionally, investors have always gravitated toward familiar assets like stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, which provide a blend of stability and growth.
However, with economic landscapes shifting, alternative investments have become increasingly popular for investors seeking ways to diversify their portfolios.
In this article, we will provide an in-depth look at both traditional and alternative investments. By understanding the differences, benefits, and risks associated with each investment option, you’ll be able to make more informed decisions about which assets best suit your financial goals.
Let’s dive in.
What Are Traditional Investments?
Traditional investments refer to well-known asset classes that are widely recognised and accessible to a broad range of investors. These assets include stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, which have long been considered foundational components of most investment portfolios due to their liquidity, transparency, and alignment with market regulations.
Traditional investments provide a relatively straightforward way for individuals to participate in the financial markets and grow their wealth.
Traditional investments are typically characterised by:
- High Liquidity: Traditional assets, particularly stocks and bonds, can be quickly bought or sold on public exchanges, providing investors with flexibility and ease of access.
- Transparency and Regulation: Traditional investments operate within established regulatory frameworks, offering investors clear, standardised information about potential risks and returns.
- Risk-Adjusted Returns: Traditional investments provide a range of risk and return levels, allowing investors to select assets that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Broad Accessibility: Traditional investments are widely accessible to retail investors, often requiring relatively low initial capital, making them suitable for individuals across various income levels.
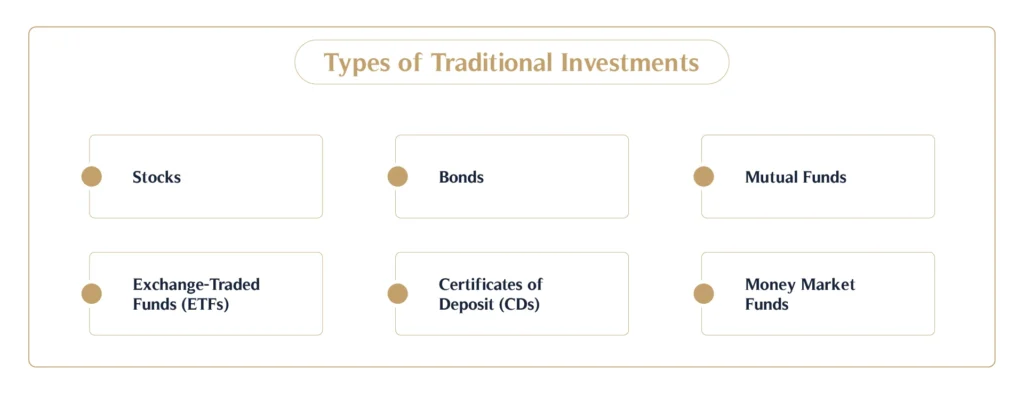
Types of Traditional Investments
- Stocks: Stocks represent ownership in a company, granting shareholders a claim on a portion of the company’s profits and assets. Stocks can offer growth potential through capital appreciation and dividends, but they also carry risk due to market volatility.
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by corporations, municipalities, or governments. When an investor purchases a bond, they are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of principal upon maturity. Bonds are generally less volatile than stocks and are often favoured by investors seeking steady income.
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool resources from multiple investors to create a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. Managed by professional fund managers, mutual funds provide an accessible, diversified investment option for retail investors who may lack the capital or expertise to invest in individual assets.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs operate similarly to mutual funds but trade on exchanges like individual stocks. ETFs offer investors exposure to a diversified portfolio of assets, often with lower management fees than mutual funds. They can be passively managed, tracking a specific index, or actively managed, depending on the investment strategy.
- Certificates of Deposit (CDs): CDs are time deposits offered by banks and credit unions, providing a fixed interest rate over a specified term. CDs are low-risk and appeal to conservative investors seeking capital preservation, though they generally offer lower returns than stocks or bonds.
- Money Market Funds: Money market funds are a type of mutual fund that invests in highly liquid, short-term debt instruments, such as Treasury bills and commercial paper. These funds are considered low-risk and provide a stable, income-generating option, though returns are modest compared to other traditional assets.
The Structure of Traditional Asset Management
Traditional investments are often managed through various account structures, including individual brokerage accounts, retirement accounts (such as IRAs and 401(k)s), and mutual fund or ETF accounts.
Asset management firms, financial advisors, and robo-advisors can assist with managing these investments, helping investors create diversified portfolios that align with their long-term financial goals.
Traditional asset management provides options for both conservative and growth-oriented investors, with numerous funds, products, and strategies available to meet different investment needs.
For those seeking a personalised approach, MHG Wealth offers expertise to help you make the most of traditional investment strategies. Learn more about how MHG Wealth can help support your investment journey.
What Are Alternative Investments?
Alternative investments such as crypto encompass a range of assets that fall outside conventional categories like stocks and bonds. These investments include tangible assets, such as real estate and commodities, as well as financial instruments like hedge funds, private equity, cryptocurrencies, and venture capital.
While diverse, alternative investments typically share several key characteristics:
- Low Liquidity: Unlike traditional investments, many alternative assets cannot be quickly converted to cash. Real estate, private equity, and art, for example, often require time to sell or exit.
- Complexity: Alternatives often employ more sophisticated strategies, involving nuanced structures and legal considerations.
- Higher Risk-Return Potential: These investments often have a higher risk profile but can also deliver significant returns, especially when traditional markets underperform.
- Diversification Benefits: Due to their low correlation with traditional assets, alternative investments can help reduce overall portfolio volatility.
Types of Alternative Investments
- Real Estate: Investing in residential, commercial, or industrial properties can yield income through rental payments or capital gains. Real estate often acts as an inflation hedge, as property values tend to increase over time.
- Hedge Funds: Hedge funds pool capital from accredited investors to pursue various strategies aimed at generating returns. These strategies can range from long-short equity positions to global macroeconomic plays, focusing on high-risk, high-reward approaches.
- Private Equity: Private equity involves investing directly in private companies or taking public companies private. The goal is to add value and eventually sell the companies at a profit. This category includes venture capital, which focuses on early-stage start-ups with growth potential.
- Private Credit: Private credit refers to non-bank loan notes provided to companies for growth, restructuring, or acquisitions. It has become an increasingly attractive asset class due to its potential for stable, high-yield returns. Investors can access expertly managed private credit opportunities through both MHG Capital and Fenchurch Legal, which provide innovative strategies in this growing sector.
- Commodities: Physical goods like precious metals (e.g., gold, silver), agricultural products, and energy resources offer a hedge against inflation and can diversify a portfolio. Commodity prices are often influenced by supply and demand, geopolitical factors, and economic shifts.
- Cryptocurrencies: Digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and other blockchain-based assets have become increasingly popular among investors. Cryptocurrencies offer high-return potential, though they are highly volatile and influenced by regulatory shifts, technological advancements, and market sentiment.
- Collectibles and Art: Tangible assets like fine art, rare coins, and luxury items have gained popularity as investment vehicles. Though speculative, these assets can appreciate significantly over time, driven by scarcity and collector demand.
The Role of Alternative Investment Partners
Investing in alternative assets often requires expertise and connections beyond what a typical retail investor might possess.
Alternative investment partners—such as advisors, fund managers, or private banks—play a crucial role by providing access, knowledge, and management strategies suited to each investor’s goals.
They help investors navigate complex assets, assess potential risks, and uncover opportunities in a fast-evolving market.
If you’re interested in exploring these opportunities, MHG Wealth offers the guidance and insights needed to make the most of alternative investments. You can also read more about how to invest in alternative investments to better understand the strategies and options available in this asset class.”
Alternative Investments vs Traditional Investments: Key Differences
Let’s explore the primary differences between alternative and traditional investments across several critical factors:
| Factor | Alternative Investments | Traditional Investments |
| Risk and Return Profiles | Often high-risk with the potential for significant returns; returns may be volatile and unpredictable. | Typically moderate risk; returns align with broader market trends and tend to be more stable. |
| Liquidity | Generally illiquid, with longer holding periods and difficulty selling quickly. | Highly liquid, enabling easy buying or selling through public markets. |
| Market Accessibility | Often limited to accredited or institutional investors, requiring substantial initial capital. | Widely accessible, with relatively low barriers to entry for individual investors. |
| Regulatory Environment | Less regulated, with varying transparency depending on asset type and jurisdiction. | Strictly regulated with robust oversight, providing greater security and standardised information. |
| Investment Horizon | Long-term focus, often requiring extended holding periods for maximum potential. | Suitable for short to long-term strategies, depending on the asset class. |
Conclusion
Alternative investments offer distinct benefits, such as potential for higher returns, diversification, and inflation protection, making them an attractive option for investors looking to reduce portfolio volatility and tap into non-traditional assets. However, these investments come with unique risks, including lower liquidity and greater complexity, often requiring specialised knowledge or guidance.
For investors considering alternative investments, it’s essential to weigh these factors against the advantages of traditional assets, which provide stability, liquidity, and accessibility within a highly regulated framework.
Choosing between alternative and traditional investments involves understanding your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Alternative investments may suit those with a long-term view and higher risk tolerance, while traditional investments often appeal to individuals seeking liquidity and lower risk. Both options, when combined thoughtfully, can create a well-rounded portfolio that balances growth and security.
In an evolving investment landscape, the alternative investment market presents a compelling opportunity for those aiming to diversify and adapt to market shifts.
For personalised advice on incorporating alternative investments into your portfolio, MHG Wealth offers the expertise and support needed to help navigate this complex terrain and tailor an investment strategy that aligns with your financial vision. Contact us today to explore how alternative investments can enrich your financial strategy.