If you’re looking to diversify your portfolio beyond traditional stocks and bonds, alternative investments offer the most potential. Among the most prominent alternative investments are private equity and hedge funds, each with distinctive strategies and objectives.
Understanding the nuances between these two investment vehicles is critical to identifying which investment aligns better with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
In this article, we’ll explore the core differences between private equity and hedge funds, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to determine which is most suitable for your investment strategy.
Key Takeaways
- Private Equity: Focuses on long-term investments in private or public companies, aiming to create value through operational improvements and strategic growth. These investments are typically illiquid and require significant capital commitments.
- Hedge Funds: Employ diverse strategies in liquid markets to achieve returns over shorter time horizons. They prioritise flexibility and active management, often appealing to investors with a higher tolerance for risk.
- Key Differences: Private equity targets long-term wealth creation and active involvement in businesses, while hedge funds offer liquidity and dynamic market strategies suited for shorter-term goals.
- Choosing the Right Option: Selecting between private equity and hedge funds depends on your financial objectives, risk tolerance, and liquidity preferences.
What is Private Equity?
Private equity refers to investments made directly in private companies or the acquisition of public companies to take them private. The primary goal of private equity firms is to create value by improving the operational efficiency, strategic direction, or market position of the companies in their portfolio.
Key Characteristics of Private Equity
- Investment Strategies: Private equity funds employ strategies that often require active management and significant time commitments:
- Buyouts: Acquiring majority or full ownership of companies, typically to streamline operations or expand into new markets.
- Growth Equity: Injecting capital into established companies seeking to scale operations without surrendering control.
- Venture Capital: Funding start-ups with high growth potential in exchange for equity stakes.
- Distressed Investments: Buying companies in financial trouble to improve performance and sell at a profit.
- Mezzanine Financing: Offering hybrid debt-equity funding to help companies grow or make acquisitions.
- Fund of Funds: Investing in private equity funds to diversify across sectors and strategies.
- Real Estate Private Equity: Acquiring, developing, and managing properties for income or appreciation.
- Illiquid Investments: Private equity investments are locked in for the fund’s lifespan, typically 7–10 years, with no early exit options.
- High Barriers to Entry: Private equity funds generally require substantial initial commitments, making them accessible only to accredited investors.
Typical Investor Profile
Private equity suits individuals and institutions with long-term investment horizons, substantial capital, and the ability to tolerate illiquidity. It often appeals to investors seeking exposure to industries or markets where they can contribute to transformational change.
What are Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds are investment vehicles designed to generate returns regardless of market conditions by employing diverse and sophisticated strategies. Unlike private equity, hedge funds primarily operate in liquid markets, focusing on short to medium-term opportunities.
Key Characteristics of Hedge Funds
- Investment Strategies: Hedge funds use a variety of sophisticated approaches to achieve returns, often adapting quickly to changing market conditions:
- Long/Short Equity: Balancing long positions in undervalued stocks with short positions in overvalued ones to manage risk and amplify returns.
- Global Macro: Leveraging macroeconomic trends, such as shifts in interest rates, currencies, or geopolitical developments.
- Arbitrage: Exploiting price inefficiencies in related securities, such as merger arbitrage or fixed-income arbitrage.
- Event-Driven Strategies: Investing based on specific events like mergers, acquisitions, restructurings, or bankruptcies, aiming to profit from market reactions to these occurrences.
- Quantitative Strategies: Using algorithms and quantitative models to identify trading opportunities across various asset classes, often involving high-frequency trading or statistical arbitrage.
- Managed Futures: Trading futures contracts based on trends in commodities, currencies, or financial markets, often using systematic models to identify opportunities.
- Multi-Strategy Funds: Employing a combination of hedge fund strategies to diversify risk and achieve more consistent returns across market conditions.
- Shorter Time Horizon: Hedge funds aim for frequent and consistent returns, offering more liquidity than private equity.
- Speculative Focus: Many hedge funds adopt strategies that involve higher risk, making them suitable for investors seeking dynamic portfolio management.
Typical Investor Profile
Hedge funds are ideal for investors with higher risk tolerance and a preference for liquidity. These funds often attract high-net-worth individuals and institutional investors looking for non-traditional, market-neutral returns.
Private Equity vs. Hedge Funds: Key Differences
The differences between private equity and hedge funds extend across various dimensions, including investment horizon, risk profile, and fees.
Here’s a closer look at how these two alternative investments compare:
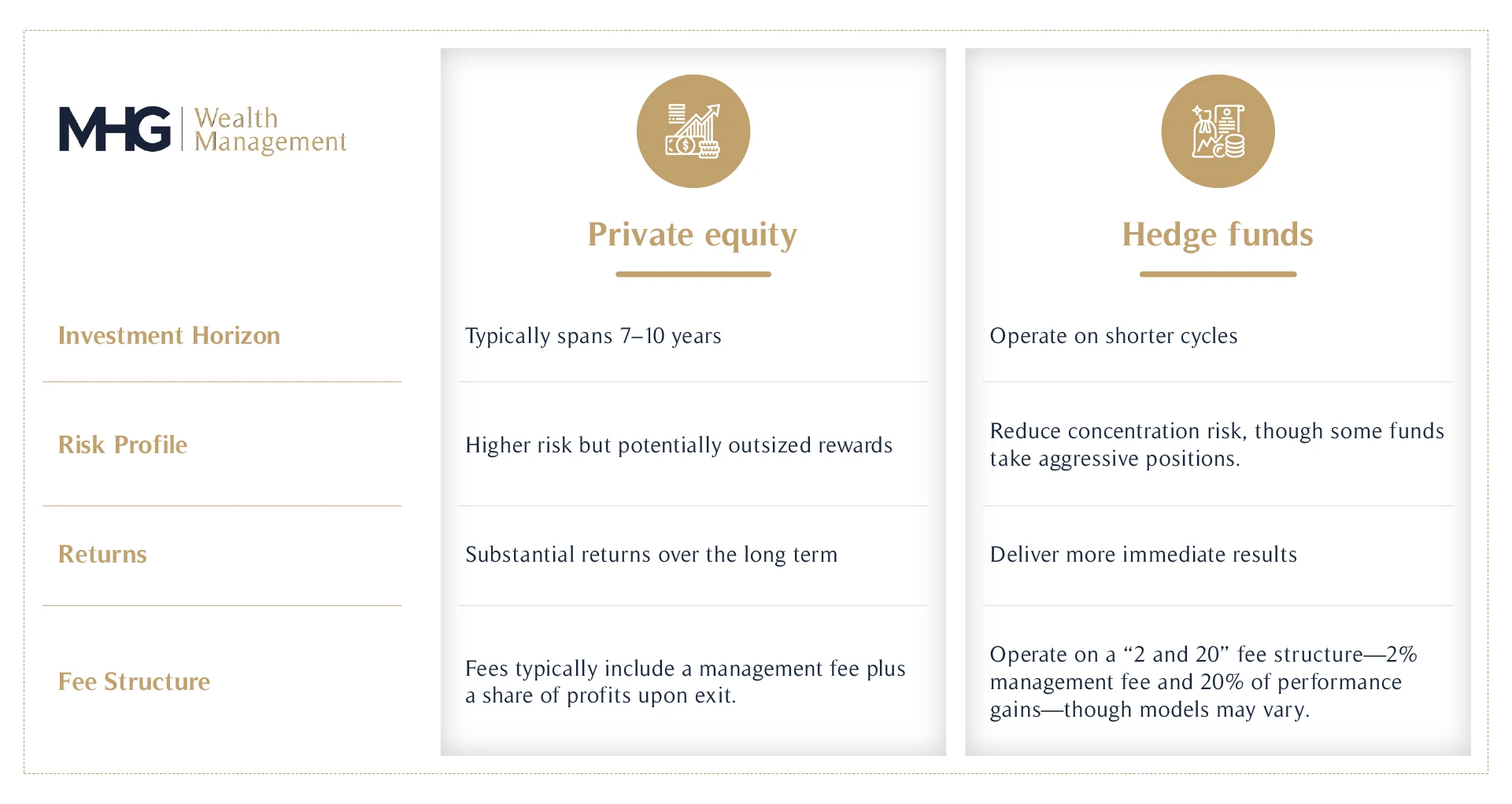
Investment Horizon
- Private Equity: Typically spans 7–10 years, as value creation through operational improvements or strategic pivots takes time to materialise.
- Hedge Funds: Operate on shorter cycles, with strategies designed to exploit near-term market opportunities.
Liquidity
- Private Equity: Investments are highly illiquid, with capital committed for the duration of the fund.
- Hedge Funds: Offer periodic redemption options, often monthly or quarterly, providing more flexibility.
Risk Profile
- Private Equity: Concentrated investments in a small number of companies, leading to higher risk but potentially outsized rewards.
- Hedge Funds: Diversified strategies reduce concentration risk, though some funds take aggressive positions.
Returns
- Private Equity: Can yield substantial returns over the long term but requires patience and a higher risk tolerance.
- Hedge Funds: Deliver more immediate results, albeit with variability depending on market conditions and strategies.
Minimum Investment Requirements and Fees
- Private Equity: High initial commitments and fees typically include a management fee plus a share of profits upon exit.
- Hedge Funds: Typically operate on a “2 and 20” fee structure—2% management fee and 20% of performance gains, though models may vary.
Private Equity vs. Hedge Funds: Advantages and Disadvantages
Both private equity and hedge funds offer distinct benefits and drawbacks, depending on the investor’s priorities.
Private Equity: Advantages
- Potential for transformative value creation and substantial returns.
- Active involvement in portfolio companies allows investors to influence outcomes.
- Access to private market opportunities.
Private Equity: Disadvantages
- Illiquidity limits flexibility.
- Significant capital requirements and extended time horizons.
- Dependence on the success of underlying companies.
Hedge Funds: Advantages
- Liquidity provides greater control over investment timelines.
- Flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions.
- Diversified strategies mitigate single-market risks.
Hedge Funds: Disadvantages
- High fees can erode returns.
- Some strategies involve substantial risk or volatility.
- Limited transparency due to proprietary investment methods.
How to Choose Which One Based on Your Financial Goals
Your choice between private equity and hedge funds should reflect your financial objectives, liquidity needs, and risk tolerance.
Goals for Wealth Preservation vs. Aggressive Growth
- Private equity aligns well with long-term wealth creation, particularly for intergenerational planning.
- Hedge funds are better suited to active investors aiming for short-term gains or market-neutral returns.
Liquidity Preferences
Investors requiring periodic access to their capital may find hedge funds more appropriate, while private equity demands a willingness to lock in funds for years.
Risk Tolerance
- Private equity’s concentrated risks appeal to those comfortable with higher stakes.
- Hedge funds offer opportunities to spread risk across markets and strategies.
Long-Term Planning
Consider how these investments fit into broader financial goals, such as retirement or estate planning:
- Private equity’s potential for outsized returns may benefit those with extended timelines.
- Hedge funds provide diversification and hedge against traditional market risks.
Private Equity vs. Hedge Funds: Final Considerations
Investing in alternative vehicles like private equity and hedge funds requires a well-informed approach. Here are some final thoughts to guide your decision:
Importance of Due Diligence
Before committing capital, thoroughly research the fund’s performance history, strategy, and management team. Understanding these elements can reduce investment risks and align expectations with reality.
The Role of Professional Advisors
Engaging a financial advisor is invaluable when determining which investment option best suits your profile. At MHG Wealth, we provide expert guidance to simplify complex decisions and help align strategies with your goals. A trusted advisor ensures your portfolio is built to meet your needs while minimising unnecessary risks.
Conclusion
Private equity and hedge funds represent two different paths within the broader category of alternative investments. Each investment offers unique opportunities and challenges, requiring investors to assess their financial goals, risk tolerance, and liquidity needs.
Private equity suits those seeking long-term wealth creation and strategic involvement in businesses. Conversely, hedge funds cater to investors aiming for liquidity, active management, and market-independent returns. Both options demand careful consideration and a commitment to understanding their complexities.
If you’re uncertain about which to pursue, consulting with a professional advisor can provide valuable insights tailored to your objectives. At MHG Wealth, we specialise in helping clients navigate alternative investments like private equity and hedge funds.
Explore our range of alternative investment products, including Fenchurch Legal and MHG Capital, designed to deliver innovative solutions for investors at all levels.
Whether you’re planning for retirement, optimising your tax strategy, or seeking new investment opportunities, our team is here to help you grow, protect, and manage your wealth. Connect with our financial experts today to discuss how we can support your investment journey and help you achieve your long-term financial objectives.